Quantum Lattice Boltzmann Method
| Project information | |
|---|---|
| Partner | Quantum Innovation Center |
| Period | September 2021 to August 2024 |
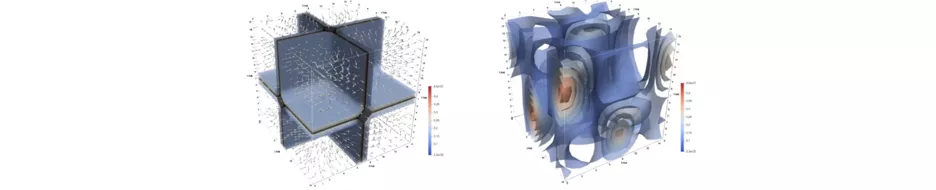
Advances in quantum hardware present new opportunities for computational fluid dynamics (CFD), a field that has historically driven the adoption of high-performance computing technologies. CFD computational paradigms have evolved from dedicated vector processors to massively parallel CPUs, GPUs, TPUs, and now to hybrid systems. These shifts highlight the necessity for co-development of CFD software, algorithms, and hardware to ensure seamless integration and avoid disruptions. Quantum computing poses a unique challenge as it fundamentally differs from classical hardware, precluding the direct transfer of established CFD models and algorithms. While dedicated quantum hardware co-design might mitigate this, universal quantum computers based on standardized quantum gates are likely to dominate in the future.
In preparation for quantum computing, we explore together with out partner Altair the potential for logarithmic compression of data and operations in CFD using quantum hardware. The Lattice-Boltzmann method (LBM), with its simple algorithmic structure and physical basis, is a promising candidate for quantum reformulation. LBM's linear streaming and non-linear collision operations can be efficiently handled by new quantum algorithms using standard quantum gates. We have successfully demonstrated the efficiency and accuracy of these algorithms for three-dimensional advection, a linear simplification of the Navier-Stokes equations, on quantum simulators. Further research aims to improve the quantum operations also for non-linear system of equations.