Hydrogen plays a central role as an energy carrier of the future. The electrolysis of water by means of a proton exchange membrane (PEM) is a promising technology for the production of green hydrogen. The operating principle of a PEM electrolyzer is based on the splitting of ultrapure water into hydrogen and oxygen by means of electric current, which can be obtained from renewable energy sources.
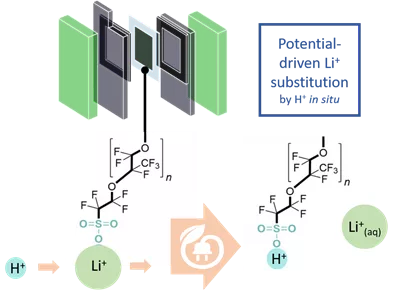
The publication shows the possibilities of modifying the standard proton exchange membrane used in PEM electrolyzers. The protons in the membrane were replaced by different metal ions (e.g. Li+, Zn2+, Ca2+) and subsequently the ion-exchanged membrane was further processed into an industrially usable MEA (membrane electrode assembly). Among other things, the ions introduced (especially Li+) have the advantage of increasing the mechanical stability during the manufacturing process. In addition, it was shown that the Li+ ions leave the membrane quantitatively during electrolysis due to the applied potential. This phenomenon was called potential-driven substitution and also helps to further improve the applicability and quality of MEAs. The authors plan to investigate further process parameters in the future and hope to stimulate further research in this area.
Morphological tuning of membrane processing by temporal proton-metal cation substitution in perfluorosulfonic acid membranes / Kim-Marie Vetter, Thomas Reichbauer, Nemanja Martić, David Reinisch, Olaf Hinrichsen, Günter Schmid / Electrochimica Acta 362 (2020) 137182, [doi]
More publications